Project Description:
The $4.4 billion CRL will provide a world-class rail service for Auckland that will have profound and long-lasting benefits for the city. The gains from building a railway tunnel and stations below central Tāmaki Makaurau are immense.
Linking the existing dead-end Britomart Station in downtown Auckland with the Western Line 3.45 kilometres away at Mt Eden and building two new train stations at Aotea and Karangahape will make the city’s electrified rail network more efficient and catching a train a more attractive and sustainable travel option. Importantly, providing a world standard rail network will reduce Auckland’s reliance on cars.
The CRL project aims to achieve sustainability excellence by being careful with the resources we use, optimising our carbon footprint, avoiding waste and leaving a positive social and cultural legacy for Tāmaki Makaurau. The CRL project’s partnership with Mana Whenua has ensured that their invaluable contribution of Māori mātauranga benefits the project and challenges us to work harder towards supporting the principles of kaitiakitanga.
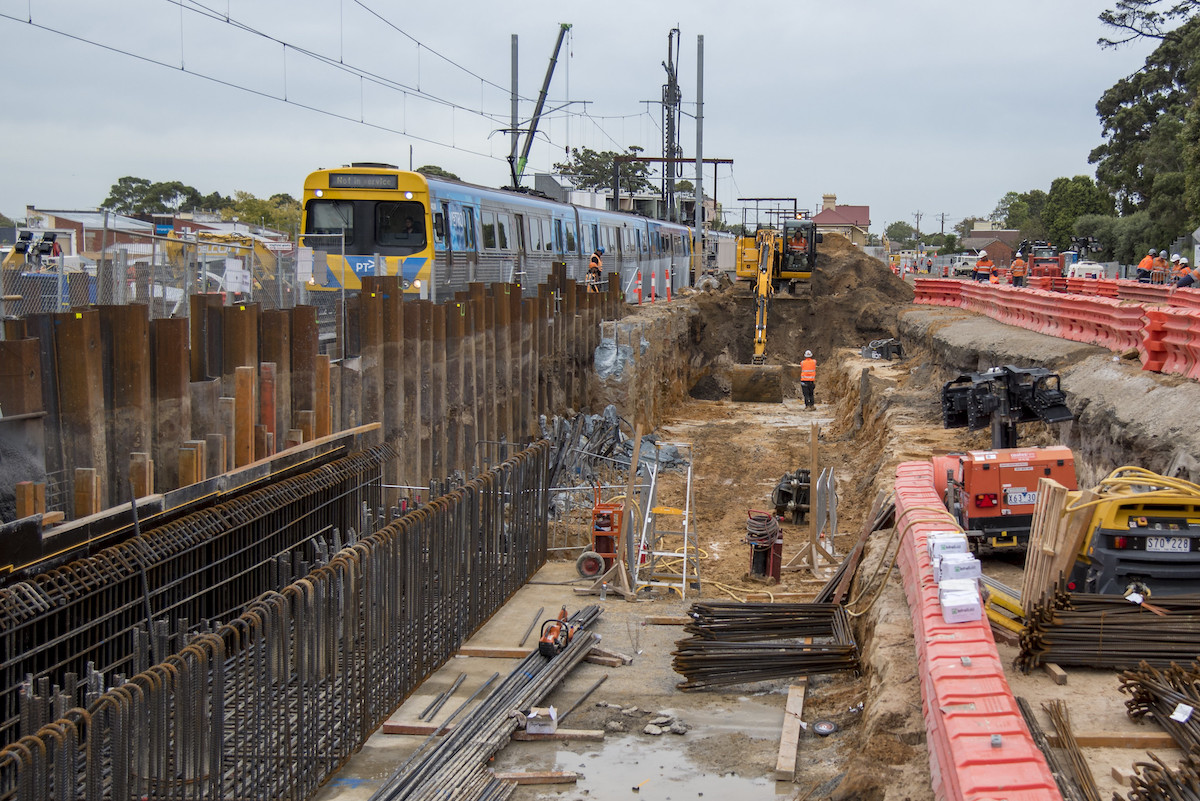
Connectus began construction on Contract 2 in 2016 with works completed in October 2020.
Contract 2 included 350 metres of trenching and tunnelling from Commercial Bay at Customs Street to Wyndham Street, relocating a stormwater main, strengthening the Ōrākei Main Sewer and improvements at street level that included wider paved footpaths, new street furniture and lighting, tree plantings and bus bays.
From the outset CRL Ltd has been determined to deliver an exemplar project – using the scale and complexity of the country’s largest transport infrastructure enterprise to push the benchmark higher for construction, workplace safety, environmental sustainability, and the reach into the community with targeted training and employment opportunities for those typically disadvantaged in the workplace.
Key Achievements:
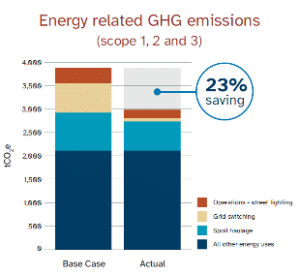
Energy Overall, Contract 2 achieved a 23 per cent reduction in GHG emissions (4,008kWh) for both the construction and operational energy-related GHG emissions combined, over CRL’s 100-year life. This figure covers Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions. When looking at just Scope 1 and 2, a 32 per cent reduction has been achieved.
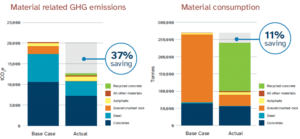
Materials A total 37 per cent reduction in materials-related GHG emissions (embodied carbon) has been achieved across both construction and the asset’s 100-year life, compared to the Base Case.
Waste Contract 2 has diverted over 97 per cent of waste from landfill. This comprises 97 per cent of all spoil, 95 per cent of all construction and demolition (C&D) waste and 75 per cent of office waste. Some 900.8 tonnes of the diverted C&D waste has been reused – including pre-cast concrete panels that were used as a traffic deck along Albert St and assorted steel on-sold to other projects.
Rating Highlights:
Highlight 1: 23% reduction in energy related GHG emissions
Overall, Contract 2 achieved a 23 per cent reduction in GHG emissions (4,008kWh) for both the construction and operational energy-related GHG emissions over CRL’s 100-year life. This figure covers Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions. When looking at just Scope 1 and 2, a 32 per cent reduction has been achieved.
Improved construction methodology reduced construction energy-related GHG emissions by 19 per cent. The most significant GHG savings were achieved by replacing diesel generators with grid electricity and using larger truck and trailer units for spoil haulage to reduce vehicle trips.
Replacing high pressure sodium lights with modern LED streetlights is projected to save 15 per cent of energy-related GHG emissions over the 100-year life of the CRL asset built by Connectus.
Highlight 2: 97% of all waste diverted from landfill
Spoil made up a significant amount of the unwanted material generated on Contract 2. In total, 97 per cent of all spoil was diverted from landfill and used to remediate Three Kings Quarry
Some 95 per cent, totalling 4,256 tonnes, of construction and demolition waste was diverted from landfill. Of this, 901 tonnes were diverted for reuse – a massive 21per cent.
Reused items included pre-cast concrete panels used as a traffic deck along Albert St and assorted steel such has propping steel that was on-sold to other projects.
Highlight 3: 37% saving in materials related GHG emissions and 11% saving in material consumption
A 37 per cent reduction in materials-related GHG emissions (embodied carbon) has been achieved across both construction and the asset’s 100-year life, compared to the Base Case.
A number of innovations significantly reduced the embodied carbon of materials used during the construction phase:
- The traffic deck at the intersection of Customs and Albert streets was redesigned to use reinforced concrete, rather than steel.
- The steelwork required to support the Albert Street excavation was reduced, and the steel struts and pre-cast traffic deck were reused.
- Backfilling was completed with recycled concrete, rather than flowable fill and fly-ash was used as a cement replacement in concrete.
Overall, Connectus achieved an 11 per cent reduction in materials used.
Acknowledgments:
International Firsts
Development of Mahi Rauora Aratohu – a tailored technical manual developed in partnership with Mana Whenua that responds to the cultural context of Tāmaki Makaurau.
State Firsts / North Island First
First use of continuous cased flight auger (CCFA) piling rig in the North Island for the temporary works piling of Albert Street.
Continuous Flight Auger (CFA) is a relatively common technique; however, the difference with the CCFA rig is the addition of a casing on a separate rotary drive which allows the full length of the bore to be cased while the auger continues to drill the pile. This methodology provides better cutting power and pile surface appearance as well as achieving better construction tolerances than the standard CFA process, with minimal vibration.
CCFA is almost vibration free and is one of the quietest piling methodologies, reducing impact on residents and nearby businesses. CCFA also reduces ground movements and consequently the risk of distress to adjacent structures such as the heritage buildings near the Connectus site. The CCFA guarantees a deviation from verticality less than 1-1.5 per cent so is suited to areas with tight tolerances in an inner-city environment. With the tight tolerances, CCFA reduces the amount of material and energy used and spoil created by reducing the risk of structural defects and the need to replace defective piles and reducing the risk of creating a larger pile than anticipated due to excessive spoil being removed through over-flighting.
This achievement is a result of the efforts of many – City Rail Link Ltd as client and ISAP, the Principal Technical Advisors, CRL Ltd’s design team, consisting of Aurecon, Mott MacDonald,Jasmax, Grimshaw and Arup and contractors Connectus, a McConnell Dowell and Downer NZ Joint Venture along with the Iwi on the CRL Mana Whenua Forum – Te Ākitai Waiohua, Te Kawerau a Maki, Ngāti Maru, Ngāti Paoa, Ngāi Tai ki Tāmaki, Ngāti Tamaoho, Ngāti Te Ata Waiohua and Ngāti Whātua Ōrākei.